Radiant Dental Arts World Class Dentistry
Arestin
Gum Disease Treatment
Periodontal disease (also known as gum disease) is a persistent dental infection that causes the bone structure that supports your teeth to deteriorate.
ARESTIN® (minocycline hydrochloride) is an antibiotic that destroys the bacteria that cause infection.
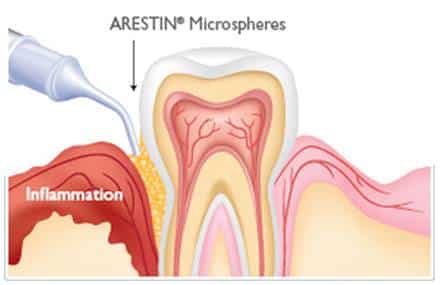
It’s inserted into the infected parts of your gums, known as “pockets.”
Brushing and flossing can’t reach the plaque and bacteria below the gum line, therefore this procedure disrupts them.
If your gums do not respond according to our expectations, we may use an antibiotic gel called Arestin to help sterilize and eliminate any dangerous germs surrounding the impacted teeth.
Plaque can convert into calculus in as little as 24 hours. If you have periodontal disease, it is essential that you visit our dentists every 3-4 months, given the seriousness of your issue.
- Oringer RJ, Al-Shammari KF, Aldredge WA, et al. Effect of locally administered minocycline microspheres on markers of bone resorption. J Periodontol 2002;73:835-842.
- Goodson JM, Gunsollwy JC, Grossi SG, et al. Minocycline HCl microspheres reduce red-complex bacteria in periodontal disease therapy. J Periodontol 2007;78(8):1568-1579.
- Williams RC, Paquette DW, Offenbacher S, et al. Treatment of periodontitis by local administration of minocycline microspheres: a controlled trial. J Periodontol 2001;72:1535-1544.

How To Brush Teeth
While brushing the outside surfaces of your teeth, position the brush at a 45-degree angle where your gums and teeth meet. Gently move the brush in a circular motion several times using small, gentle strokes. Use light pressure while putting the bristles between the teeth, but not so much pressure that you feel any discomfort.
When you are done cleaning the outside surfaces of all your teeth, follow the same directions while cleaning the inside of the back teeth.
To clean the inside surfaces of the upper and lower front teeth, hold the brush vertically. Make several gentle back-and-forth strokes over each tooth. Don’t forget to gently brush the surrounding gum tissue.
Next you will clean the biting surfaces of your teeth by using short, gentle strokes. Change the position of the brush as often as necessary to reach and clean all surfaces. Try to watch yourself in the mirror to make sure you clean each surface. After you are done, rinse vigorously to remove any plaque you might have loosened while brushing. If you have any pain while brushing or have any questions about how to brush properly, please be sure to call our office.
How To Floss
Periodontal disease usually appears between the teeth where your toothbrush cannot reach. Flossing is a very effective way to remove plaque from those surfaces. However, it is important to develop the proper technique. The following instructions will help you, but remember it takes time and practice.
Start with a piece of floss (waxed is easier) about 18″ long. Lightly wrap most of the floss around the middle finger of one hand. Wrap the rest of the floss around the middle finger of the other hand.
To clean the upper teeth, hold the floss tightly between the thumb and forefinger of each hand. Gently insert the floss tightly between the teeth using a back-and-forth motion. Do not force the floss or try to snap it in to place. Bring the floss to the gum line then curve it into a C-shape against one tooth. Slide it into the space between the gum and the tooth until you feel light resistance. Move the floss up and down on the side of one tooth. Remember there are two tooth surfaces that need to be cleaned in each space. Continue to floss each side of all the upper teeth. Be careful not to cut the gum tissue between the teeth. As the floss becomes soiled, turn from one finger to the other to get a fresh section.
To clean between the bottom teeth, guide the floss using the forefinger of both hands. Do not forget the backside of the last tooth on both sides, upper and lower.
When you are done, rinse vigorously with water to remove plaque and food particles. Do not be alarmed if during the first week of flossing your gums bleed or are a little sore. If your gums hurt while flossing you could be doing it too hard or pinching the gum. As you floss daily and remove the plaque your gums will heal and the bleeding should stop.
Caring for Sensitive Teeth
Choosing Oral Hygiene Products
Sometimes after dental treatment, teeth are sensitive to hot and cold. This should not last long, but only if the mouth is kept clean. If the mouth is not kept clean, the sensitivity will remain and could become more severe. If your teeth are especially sensitive, consult with your doctor. They may recommend a medicated toothpaste or mouth rinse made especially for sensitive teeth.
There are so many products on the market that it can become confusing, and choosing between all the products can be difficult. Here are some suggestions for choosing dental care products that will work for most patients.
Automatic and “high-tech” electronic toothbrushes are safe and effective for the majority of the patients. Oral irrigators (water spraying devices) will rinse your mouth thoroughly, but will not remove plaque. You need to brush and floss in conjunction with the irrigator. We see excellent results with electric toothbrushes
Called Rotadent and Interplak. Some toothbrushes have a rubber tip on the handle. This is used to massage the gums after brushing. There are also tiny brushes (interproximal toothbrushes) that clean between your teeth. If these are used improperly you could injure the gums, so discuss proper use with Dr. Avina.
Fluoride toothpastes and mouth rinses, if used in conjunction with brushing and flossing, can reduce tooth decay as much as 40 percent. Remember, these rinses are not recommended for children under six years of age. Tartar control toothpastes will reduce tartar above the gum line, but gum disease starts below the gum line so these products have not been proven to reduce the early stages of gum disease.
Anti-plaque rinses, approved by the American Dental Association, contain agents that may help bring early gum disease under control. Use these in conjunction with brushing and flossing.
Nutrition
Good nutrition plays a large role in your dental health. Brushing and flossing help keep your teeth and gums healthy and strong. However, a balanced diet will help to boost your body’s immune system, leaving you less vulnerable to oral disease.
How often and what you eat have been found to affect your dental health. Eating starchy foods such as crackers, bread, cookies, and candy causes the bacteria in your mouth to feed on it. They then produce acids which attack your teeth for up to 20 minutes or more. Foods that stick to your teeth or are slow to dissolve give the acids more time to work on destroying your tooth enamel.
Sticky/slow to dissolve foods:
- granola bars
- chewy fruit snacks
- dried fruit
- potato chips
- hard candy
Starchy foods:
- crackers
- breads
- cookies
- candy
Sticky and starchy foods create less acid when eaten as part of a meal. Saliva production increases at mealtime, rinsing away food particles and neutralizing harmful acids.
Foods such as nuts, cheese, onions, and some teas have been shown to slow growth of decay-causing bacteria in the mouth.
SCHEDULE A CONSULTATION
Come in for a consultation and find out all about the best cosmetic dentist in San Diego, CA. Let Dr. Avina help you own your smile.
